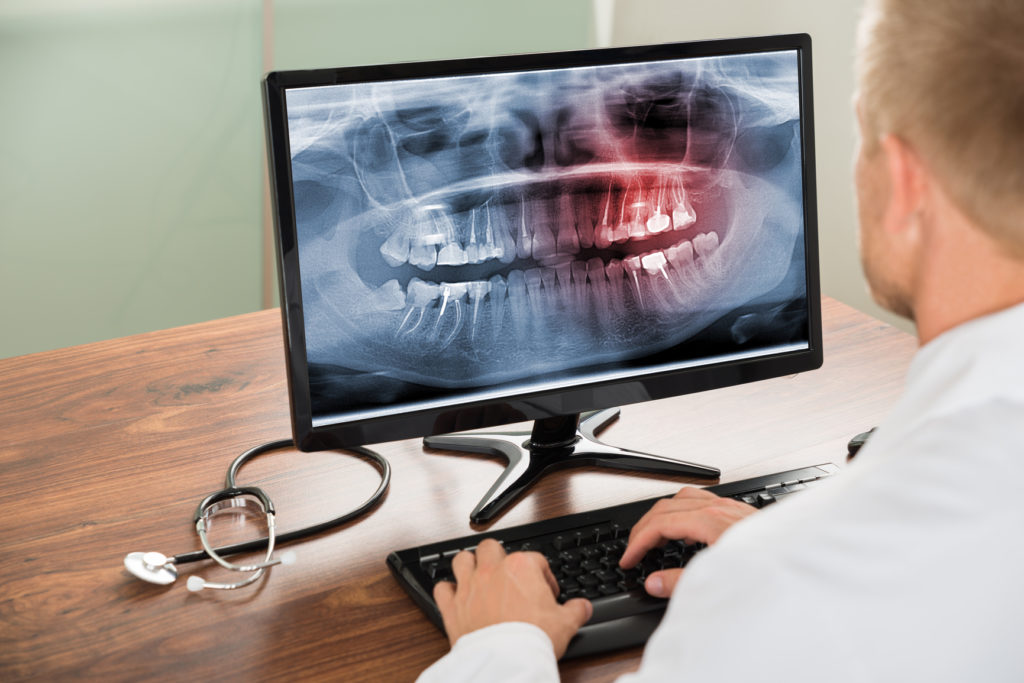
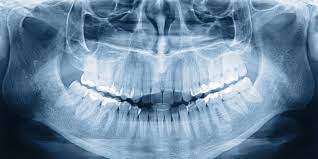
Dental X-rays, also known as dental radiographs, are an essential diagnostic tool used by dentists and general denstistry to gain insight into your oral health beyond what is visible during a regular dental examination. These images allow dentists to detect and diagnose various dental issues, ranging from cavities to hidden dental problems beneath the gum line. In this blog, we will delve into everything you need to know about dental X-rays, their different types, benefits, safety measures, and why they play a crucial role in maintaining your overall oral health.
Understanding Dental X-Rays
Dental X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, similar to the X-rays used in medical imaging. When X-rays pass through the oral structures, they create images that highlight the differences in density between the teeth, bones, and soft tissues. These images help dentists identify potential problems not visible to the naked eye, enabling them to devise appropriate treatment plans.
Types of Dental X-Rays
There are several types of dental X-rays, each serving a specific purpose:
a. Bitewing X-rays: These X-rays capture the upper and lower back teeth and are used to detect cavities, tooth decay, and bone loss.
b. Periapical X-rays: Periapical X-rays provide a detailed view of individual teeth, including the roots and surrounding bone. They help diagnose issues like abscesses and impacted teeth.
c. Panoramic X-rays: Panoramic X-rays give a broad view of the entire mouth, including the jawbone, teeth, sinuses, and temporomandibular joints (TMJ). These X-rays are useful for assessing overall oral health and planning orthodontic or implant procedures.
d. Occlusal X-rays: Occlusal X-rays capture a broad view of the floor or roof of the mouth, helping identify issues such as cleft palate or extra teeth.
e. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT): CBCT is a three-dimensional imaging technique that provides detailed images of the teeth, bones, nerves, and soft tissues. It is commonly used in implant planning, oral surgeries, and complex dental cases.
Benefits of Dental X-Rays
Dental X-rays offer several benefits in diagnosing and treating oral health conditions:
a. Early Detection: X-rays can reveal dental problems in their early stages, allowing dentists to address issues before they become more serious and require extensive treatment.
b. Comprehensive Assessment: X-rays provide a comprehensive view of your oral structures, helping dentists analyze the condition of your teeth, roots, jawbone, and supporting tissues.
c. Treatment Planning: X-rays assist dentists in creating personalized treatment plans that suit your unique oral health needs, ensuring effective and targeted care.
d. Monitoring Progress: For patients undergoing orthodontic treatment or dental implants, X-rays help dentists monitor the progress and make necessary adjustments along the way.
Safety Measures and Radiation Exposure
Concerns about radiation exposure are natural when it comes to X-rays. However, dental X-rays use very low levels of radiation, and dentists take precautions to minimize exposure. Some safety measures include:
a. Lead Aprons: Patients are provided with lead aprons to cover the body during X-rays, reducing exposure to other areas not being imaged.
b. Digital X-rays: Digital X-ray technology significantly reduces radiation exposure compared to traditional film X-rays. It also offers instant image results, promoting faster diagnosis and treatment planning.
c. Selective Use: Dentists follow the "ALARA" principle (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) and only recommend X-rays when necessary, based on individual risk factors and oral health history.
Frequency of Dental X-Rays
The frequency of dental X-rays varies based on a patient's oral health needs and risk factors. Generally, new patients may require a set of X-rays to establish a baseline, while existing patients might undergo X-rays annually or every few years, depending on their dental health status and any changes or concerns identified.
Dental X-Rays and Children
Pediatric patients may require X-rays more frequently than adults due to their changing dentition and higher susceptibility to tooth decay. However, dentists are cautious and use lead aprons to protect children during X-rays. Digital X-rays, with lower radiation exposure, are often preferred for young patients.
Pregnancy and Dental X-Rays
If you are pregnant or suspect you might be pregnant, it is essential to inform your dentist. Although dental X-rays use low radiation levels and lead aprons protect against exposure, X-rays are generally avoided during pregnancy, especially during the first trimester, unless deemed necessary for a dental emergency.
Conclusion
Dental X-rays are a vital tool in modern dentistry, providing valuable insights into your oral health and aiding in early detection and treatment of dental issues. With advancements in technology and safety measures, the risks associated with dental X-rays are minimal, and the benefits far outweigh any concerns. Regular X-rays, in combination with routine dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices, contribute to maintaining a healthy and radiant smile for years to come. Remember, open communication with your dentist about your dental history and any specific concerns will ensure a tailored approach to your oral health needs.